Research Article - (2021) Volume 12, Issue 11
Effectiveness of Bacopa Herb for Solving Dementia in the Elderly
Wuttiphong Phakdeekul* and Warinmad KedthongmaAbstract
Background: Dementia in the elderly has become a problem in health, medicinal plants, have been used to cure several human diseases.
Methods: The study used pretest-posttest control group design research from September 2020 to March 2021 based on phases of before and after herbal treatment. Samples were 361 elderly, randomly selected using cluster random sampling. Data were collected based on an Abbreviated Mental Test (AMT) and the Barthel index of Activities of Daily Living (ADL) which were then analyzed using Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient, multiple regression, and a paired t-test.
Results: The results revealed that most samples had dementia at an abnormal level (40.50%), 91.50% had no record of a relative with dementia, and had an ADL score of ‘help themselves and help others. In addition, age and stress were related to dementia in the elderly, with statistical significance at α =0.01 (r=0.224 and r=0.636, respectively). Moreover, these factors can be used to predict dementia with 51.1% (R2=0.511; p<0.0001) of the total variance of dementia in the elderly. The effectiveness of the bacopa herb was confirmed by a reduction in the dementia level from 40.50% to only 24.68% (p<0.0001) and the ADL was increased to 89.24% (p<0.0001).
Conclusion: Age and stress had a major effect on dementia. Therefore, a daily capsule that contains the herbs Bacopa monnieri and Centella asiatica and germinating rice and turmeric could benefit brain activity, which were supported by increases in AMT and ADL.
Keywords
Elderly, Dementia, Quality of life, Bacopa herb, AMT, ADL
Introduction
The number of elderly people is increasing so that changes in both physical and mental health are inevitable and may cause several health disorders (Kowal P and Dowd JE, 2001). Dementia is considered to be a neurodegenerative disorder that is characterized by increased oxidative stress. Medicinal plants, with their antioxidant properties, have been used to cure several human diseases. Dementia in the elderly has become a common occurrence. There are several traits for dementia, including memory loss (both short and long term), declining ability to learn new things, and changes in daily behavior. These traits can be gradually observed. Recently, several studies have suggested that factors that promote the risk of dementia include sex, age, education, body mass index, disease, accidents, genetics, lack of exercise, excess alcohol, and stress (Alzheimer's Association, 2012; Baumgart M, et al., 2015; Larson EB, et al., 2013; Håkansson K, et al., 2009). Stress in the elderly is caused by both internal and external factors which normally affect happiness and cause discomfort at different levels for different people. This stress is directly related to dementia in the elderly (Ryan J, et al., 2008; Sakuldach M, et al., 2020; Phakdeekul W and KedThongma W, 2019; Sardsaengjun C, 2013).
Treatment includes medicine, rehabilitation, and the use of herbs. Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. and Centella asiatica (L.) have been used in treatments due to the ingredients triterpenoid saponin and bacoside that aid in memory in the elderly. Studies in 2013 and 2016 showed that when the elderly (aged 55 and above) consumed 300-450 g daily there was a significant decrease in memory loss without further side effects (Dhanasekaran M, et al., 2007; Pongpom M, et al., 2013; Nuss P, et al., 2009; Hamon A, et al., 2003; Heysieattalab S, et al., 2016; Korpi ER and Sinkkonen ST, 2006).
Recent studies showed the consumption of Centella asiatica reduced memory loss and promoted brain activity in children similar to gingko and has already been commercialized in capsule form (Dhanasekaran M, et al., 2015; Anekonda TS and Reddy PH, 2005). GABA or Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid is an amino acid that acts as neurotransmitter to inhibit and balance the neurotransmitter system. When consumed, it promotes calmness and reduces stress as well as reducing jitteriness. In addition, it was reported to prevent Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, act as an anticancer ingredient, to reduce stress disorder, insomnia, epilepsy, headaches, and blood pressure and to increase brain metabolism, by ameliorating thick artery walls and abnormal blood circulation which may cause a rupture of a blood vessel. The recommended amount is 750-1,950 mg per day. Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) is a potent antioxidant ingredient due to its major component of tyrosine, which can be used for detoxifying and to reduce inflammation. The World Health Organization has registered turmeric as an ingredient for treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and to address symptoms of vein thrombosis. Tyrosine also promotes the production of serotonin which improves sleep soundness and reduces depression by converting to melatonin (Lieberman HR, et al. McLean A, et al., 2004; Fernstrom JD and Fernstrom MH, 2007). Psychiatric symptoms and mental health may be caused by genetic factors, a dysfunction in brain activity, social pressures, and mental instability (Thomsen PH, 1996; Lazarus RS and Folkman S, 1984; Phakdeekul W, et al., 2011). To treat such disorders, it is important to reduce the effects of these factors (Yiengprugsawan V, et al., 2012; Foundation for Thai Gerontology Research and Development, 2009). Global estimations of the burden of disease show that mental illness plays a prominent role. Elderly club is one of the several ways to promote social interaction, gain self-esteem, slow progression of physical and mental disabilities in old age people. Furthermore, in Sakon Nakhon province, Thailand there is an increasing trend per capita of dementia in the elderly. In 2017, approximately half the elderly (12.9% of the population) showed sign of dementia. In 2018, 0.9% from 13.5% and 1.40% from 14.6% in 2019 were reported (Apidechkul T, 2011; Kosulwit L, 2012; Turner III DW, 2010). Therefore, in the present study, we aimed to evaluate the factors predicted dementia in the elderly, and the effectiveness of herbs in the treatment of dementia in the elderly in Sakon Nakhon province, Thailand.
Materials and Methods
This study investigated the effectiveness as a treatment for dementia in the elderly of a combination of herbs that had been classified as safe for human consumption and had already been proven in clinical testing. The study used pretest-posttest control group design research during September 2020 to March 2021 based on phases of before and after herbal treatment.
Phase I
Cross-sectional survey research: The target population was 1,897 elderly people older than 60 years with reported dementia in Sakon Nakhon province. The number of samples was calculated based on the following equation using cluster random sampling; the design effect was multiplied by n to produce a sample size of 316 individuals (Turner III DW, 2010; Hsieh FY, et al., 1998). Samples were enrolled through cluster random sampling from two sets of data (large and small districts) in Sakon Nakhon province, with Mueang districts representing the large, and Kusuman small districts, respectively. The names of the elderly were placed in a container and drawn at random according to the required sample size (Table 1).
| District | N | n |
|---|---|---|
| Mueang | 426 | 271 |
| Kusuman | 69 | 45 |
Table 1: Probability proportional to size of elderly with dementia
Inclusion criteria: It consisted of
• Elderly with dementia older than 60 years within the two subdistricts of the study
• Able to read and write to complete the survey, and
• Willing to answer the study questions.
Exclusion criteria: It consisted of:
• Any unexpected situation that meant the interview could not continue and
• Participant’s desire to leave the program.
Phase II
Experimental research: Pretest-posttest Control Group Design Research: In this phase, 316 individuals were given the herbal treatment consisting of a capsule of a combination of herbs at 750 mg or BRAHMIX. This product was formed and packed in a facility accredited with GMP by the Food and Drug Administration. Each subject had to be willing to take the capsule daily and was monitored by public health personnel for side effects during the 6 months of study. After the herbal treatment, each subject was evaluated again using the AMT and ADL tests.
Research tools
Tools for analysis consisted of 4 parts. First was basic personal information (sex, age, education, financial status, personal health, and record of health program). Second was the stress level record from Suanprung hospital (Suanprung Stress Test-20, SPST-20). The test consists of 20 questions with a maximum possible score of 100. The test was used to evaluate the recent stress level from daily activities during the past 6 months prior to the test date. Scores were classified into 4 categories: 0-23 was categorized as low stress; 24-41 was categorized as moderate stress; 42-61 was categorized as high stress; and above 62 was categorized as severe. The third part was the brain condition test determined using the Abbreviated Mental Test (AMT) from the Institute of Geriatrics, Department of Medical Services, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. This test consists of 10 questions with a score less than or equal to 7 considered as abnormal and above 8 points considered as normal. For part four, the Barthel Index of ADL was used to identify an individual’s ability to perform daily activities (Ministry of Public Health, 2019). Scores were categorized into three separate groups: 0-4, indicated the target was unable to carry out normal daily activities and required assistance; 5-11, indicated moderate assistance was required but could perform most basic activities; and 12 and higher, categorized as normal. The Department of Medical Services uses the stress level questionnaire SPST-20 to determine AMT and ADL with Cronbach’s Alpha coefficients of 0.86, 0.82, and 0.87. However, due to preliminary experiment, these coefficients were adjusted to 0.79, 074, and 0.89, respectively.
Data collection
Public health officers from both the district and subdistrict assisted in collecting data from the 316 elderly participants before and after herbal treatment.
• Data were collected during interviews to evaluate stress level and brain condition using the Abbreviated Mental Test (AMT). Activities of Daily Living (ADL) were assessed using the Barthel index. Each participant was asked to answer a control question within 30 minutes.
• Follow up and monitoring was done once a month by checking the food record book when distributing the dietary supplement products
• After 6 months of treatment, the stress level and brain condition tests were repeated.
• Data were checked and recollected if necessary.
• Data were coded and filed.
• Data were evaluated statistically and analyzed.
Data analysis
The intention to treat analysis method (descriptive statistics) was used which considered the frequency, percentage, average, and standard deviation in the analysis. Inferential statistics were used to identify factor correlation by interval and ratio based on bi-variable analysis and the Pearson‘s product moment correlation coefficient. Multiple regression was used to evaluate the factors influencing dementia in the elderly and ADL. All data were then compared using a paired t-test.
Ethics
This research was approved by authorities from the Provincial Health Office, Sakon Nakhon (SKN REC 2020-001), and registration at Thai Clinical Trials Registry (TCTR) since 2020-08-25 22:05:57. TCTR identification number is TCTR20200903007.
Results
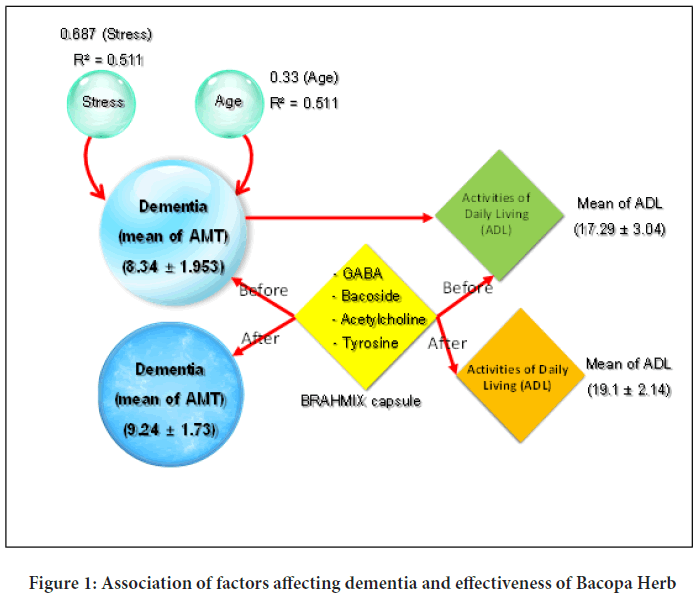
The majority of elderly participants in this study was female and aged 60-72 years old (69.60%), with the average age being 70.1 years (66.82%) of the total studied population. Most (92.79%) of the sample had a highest education level at primary school, 90.82% faced a financial problem, and 86.40% had a personal health problem other than dementia. Of the sample, 40.50% had signs of dementia, 90.89% were in the elderly care program, and 91.50% did not have any relative with a record of dementia. Age and stress level each had a significant influence on dementia in the elderly (α =0.01, r=0.224:p<0.0001 and r=0.636:p<0.0001, respectively) as shown in Table 2. These factors can be used to predict the potential of dementia with R2=0.511 (p<0.0001) as shown in Table 3.
| Factor | Related to elderly dementia | |
|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient (r) | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.224** | <0.0001 |
| Stress | 0.636** | <0.0001 |
Note: **significance at 0.01 level
Table 2: Correlation coefficient of elderly dementia
| Predictive variable | Non standard regression coefficient | Standard regression coefficient | t | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| Age | 0.038 | 0.005 | 0.33 | 8.246 | <0.0001** |
| Stress | 0.272 | 0.016 | 0.687 | 17.18 | <0.0001** |
| Constant | -0.363 | 0.365 | -6.465 | 0.003* | |
R=0.715, R2=0.511, Adjusted R2=0.508, SE=0.6017
Note: *significance at 0.05 level, **significance at 0.01 level
Table 3: Stepwise multiple regression analysis of predictive variables of elderly dementia (n=136)
The dementia level before treatment (40.50%) was reduced to 24.68% after herbal treatment, as shown in Table 4. The AMT showed an increase in brain condition (Table 5). In addition, a slight increase was observed in activities of daily lives after herbal treatment from 84.81% to 89.21%, as shown in Table 6. After herbal treatment, the elderly could conduct their daily routine without needing support, as shown in Table 7.
| Before project | After project | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (percentage) | x | SD. | Frequency (percentage) | x | SD. |
| 188 (59.50) | 8.54 | 2.04 | 238 (75.32) | 9.01 | 2.61 |
| 128 (40.50) | 6.32 | 1.61 | 78(24.68) | 7.64 | 1.09 |
| 316(100.0) | 8.34 | 1.953 | 316(100.0) | 9.24 | 1.73 |
Table 4: Average AMT of participants before and after project (n=316)
| Variable | n | x | SD. | 95%CI | t | (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Before project | 316 | 8.34 | 1.953 | -1.732 | 1.0471 | 4.308 | 0.0001 |
| After project | 316 | 9.24 | 1.73 | ||||
Note: **significance at 0.01 level
Table 5: Comparison of AMT before and after project (n=136)
| ADL score | Before project | After project | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (percentage) | x | SD. | Frequency (percentage) | x | SD. | |
| 12 or more | 268 | 17.46 | 2.61 | 282 | 19.46 | 2.74 |
| -84.81 | -89.24 | |||||
| 5-11 | 32 | 7.49 | 2.05 | 24 | 12.05 | 2.18 |
| -10.13 | -7.59 | |||||
| Less than 5 | 16 | 3.24 | 0.52 | 10 | 6.81 | 1.02 |
| -5.06 | -3.16 | |||||
| Total Score | 316 | 17.29 | 3.043 | 316 | 19.1 | 2.14 |
| -100 | -100 | |||||
Table 6: Average ADL before and after project (n=316)
| Variable | n | x | SD. | 95%CI | t | (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Before project | 316 | 17.29 | 3.043 | -2.791 | 1.51 | -10.108 | 0.0001 |
| After project | 316 | 19.1 | 2.14 | ||||
Note: **significance at 0.01 level
Table 7: Comparison of AMT before and after project (n=136)
Discussion
Preliminary investigation revealed that stress level and age were the two major factors influencing dementia in the elderly and could be used to predict potential dementia with 51.1% accuracy, but in the pass time little was known about adherence to antidepressant treatment during acute and continuation phase of depression among older adults with dementia and newly diagnosed major depressive disorders (Ministry of Public Health, 2019; Bhattacharjee S, et al., 2020). Which was similar to other studies found that more than one-third of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Psychiatric patients used inappropriate antipsychotics among those who were treated with atypical antipsychotic medications. Various socio-demographics and clinical factors were associated with inappropriate antipsychotic use in older patients with PD. Concerted efforts are needed to reduce inappropriate atypical antipsychotic use (Chekani F, et al., 2020; Wang J, et al., 2019; Piyabhan P and Wetchateng T, 2013). However, the several study reported the stress level of the elderly and mental health were not correlated. For example, dementia is not included in the government-subsidized Community Health Service (CHS) package, and currently, there is few public health care program specifically for dementia in China. For dementia family, extra resources are still belonging to paid services (Wang J, et al., 2019; Piyabhan P and Wetchateng T, 2013; Piyabhan P and Wetchateng T, 2015; Uabundit N, et al., 2010). Then, the current is study found a correlation between dementia and the age/stress level of the elderly with accuracy of 51.1% yielding an AMT score of 8.34 ± 1.953 with 40.50% having dementia that affected their daily life with a score of 17.29 ± 3.04 and elderly participants with disability accounting for 15.19% with an ADL score below 11. After participating in the herbal treatment program, the AMT increased to 9.24 ± 1.73 and the ADL increased to 19.1 ± 2.14, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Association of factors affecting dementia and effectiveness of Bacopa Herb
In addition, there were several studies that used Bacopa monnieri as medicine to treat Alzheimer’s disease and to restore memory in patients with schizophrenia (Saini N, et al., 2019; Saini N, et al., 2012). Another finding from the current is study was that the quality of life of the elderly increased if they did not require support. These herbs (Bacopa monnieri wettst, Centella asiatica, Gaba and turmeric), improved memory and reduced panic and reduce depression. Similar findings were reported for a combination of these herbs (Deplanque D, et al., 2018; Poisbeau P, et al., 2018; Mattei C, et al., 2019; Poonsawang T, et al., 2020; Nueakhumung J, et al., 2020; Van Patten R, et al., 2020; Batko-Szwaczka A, et al., 2020). Not only, herbal therapy was used for elderly care but also could be closely care by public health volunteers, and applied participation technology (Chekani F, et al., 2020). Such as, aging populations across the globe are in need of creative, innovative treatments in order to support health and wellness in the later stages of life, a higher probability of Composite Endpoint (CE). It was associated with age ≥ 70 years (P=0.018), taking any medication or supplements (P=0.007). Therefore, concerted efforts are needed to reduce inappropriate atypical antipsychotic use among elderly patients.
Conclusion
Age had a major effect on dementia. Therefore, it is important to start monitor the elderly at an early stage by reducing stress and provide supplements to the diet that prevent dementia. A daily capsule that contains the herbs Bacopa monnieri and, Centella asiatica and germinating rice and turmeric could benefit brain activity as shown by an improvement in mood, aiding sleep, reducing depression, and improving memory, which were supported by increases in AMT and ADL. The authors plan to conduct further study at the cellular level to investigate brain activity.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute, Thailand for providing financial support for this project, and to staff in the Public Health Department in Sakon Nakhon province who facilitated the study and provided official support.
Disclosure
Assistant Professor Dr. Wuttiphong Phakdeekul reports grants from Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute, during the conduct of the study. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- Kowal P, Dowd JE. Definition of an older person. Proposed working definition of an older person in Africa for the MDS Project. World Health Organization. 2001; 10(2.1): 5188-9286.
- Alzheimer's Association. 2012 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2012; 8(2): 131-168.
- Baumgart M, Snyder HM, Carrillo MC, Fazio S, Kim H, Johns H. Summary of the evidence on modifiable risk factors for cognitive decline and dementia: a population-based perspective. Alzheimers Dement. 2015; 11(6): 718-726.
- Larson EB, Yaffe K, Langa KM. New insights into the dementia epidemic. New Eng J Med. 2013; 369(24): 2275.
- Håkansson K, Rovio S, Helkala EL, Vilska AR, Winblad B, Soininen H, et al. Association between mid-life marital status and cognitive function in later life: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2009; 339.
- Ryan J, Croft K, Mori T, Wesnes K, Spong J, Downey L, et al. An examination of the effects of the antioxidant Pycnogenol® on cognitive performance, serum lipid profile, endocrinological and oxidative stress biomarkers in an elderly population. J Psychopharmacol. 2008; 22(5): 553-562.
- Sakuldach M, Kedthongma K, Phakdeekul W. Comparisons Health Literacy to the Performance of Volunteers in Elderly Care, Pad Subdistrict Municipality, Kham Ta Kla District, Sakon Nakhon Province. Test Eng Manag. 2020; 83: 16398-16400.
- Phakdeekul W, KedThongma W. Drug Relapse Therapy with Herbs. Isan J Pharm Sci. 2019; 15(3): 104-112.
- Sardsaengjun C. Bacopa: herb for brain health. Thammasat Medical Journal. 2013; 13(4): 554-560.
- Dhanasekaran M, Tharakan B, Holcomb LA, Hitt AR, Young KA, Manyam BV. Neuroprotective mechanisms of ayurvedic antidementia botanical Bacopa monniera. Phytother Res. 2007; 21(10): 965-969.
- Pongpom M, Sawatdeechaikul P, Kummasook A, Khanthawong S, Vanittanakom N. Antioxidative and immunogenic properties of catalase-peroxidase protein in Penicillium marneffei. Med Mycol. 2013; 51(8): 835-842.
- Nuss P, Ferreri F, Bourin M. An update on the anxiolytic and neuroprotective properties of etifoxine: from brain GABA modulation to a whole-body mode of action. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019; 15: 1781.
- Hamon A, Morel A, Hue B, Verleye M, Gillardin JM. The modulatory effects of the anxiolytic etifoxine on GABAA receptors are mediated by the β subunit. Neuropharmacology. 2003; 45(3): 293-303.
- Heysieattalab S, Naghdi N, Hosseinmardi N, Zarrindast MR, Haghparast A, Khoshbouei H. Methamphetamine‐induced enhancement of hippocampal long‐term potentiation is modulated by NMDA and GABA receptors in the shell–accumbens. Synapse. 2016; 70(8): 325-335.
- Korpi ER, Sinkkonen ST. GABAA receptor subtypes as targets for neuropsychiatric drug development. Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 109(1-2): 12-32.
- Dhanasekaran S, Perumal P, Palayan M. In-vitro Screening for acetylcholinesterase enzyme inhibition potential and antioxidant activity of extracts of Ipomoea aquatica Forsk: therapeutic lead for Alzheimer’s disease. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2015; 5: 12-16.
- Anekonda TS, Reddy PH. Can herbs provide a new generation of drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease?. Brain Res Rev. 2005; 50(2): 361-376.
- Lieberman HR, Thompson LA, Caruso CM, Niro PJ, Mahoney CR, McClung JP, et al. The catecholamine neurotransmitter precursor tyrosine increases anger during exposure to severe psychological stress. Psychopharmacology. 2015; 232(5): 943-951.
- McTavish SF, McPherson MH, Harmer CJ, Clark L, Sharp T, Goodwin GM, et al. Antidopaminergic effects of dietary tyrosine depletion in healthy subjects and patients with manic illness. Br J Psychiatry. 2001; 179(4): 356-360.
- McLean A, Rubinsztein JS, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ. The effects of tyrosine depletion in normal healthy volunteers: implications for unipolar depression. Psychopharmacology. 2004; 171(3): 286-297.
- Fernstrom JD, Fernstrom MH. Tyrosine, phenylalanine, and catecholamine synthesis and function in the brain. J Nutr. 2007; 137(6): 1539S-1547S.
- Thomsen PH. Schizophrenia with childhood and adolescent onset-a nationwide register‐based study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1996; 94(3): 187-193.
- Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping. Springer. 1984.
- Phakdeekul W, Thongkrajai P, Eiamprapai P, Kanato M. Risk factors to alcohol law violations in the community: Quasi-experimental study. Am J Appl Sci. 2011; 8(12): 1343.
- Yiengprugsawan V, Somboonsook B, Seubsman SA, Sleigh AC. Happiness, mental health, and socio-demographic associations among a national cohort of Thai adults. J Happiness Stud. 2012; 13(6): 1019-1029.
- Foundation for Thai Gerontology Research and Development. Foundation of Thai Gerontology Report 2009. Bangkok: Ministry of Social Development and Human Security. 2009.
- Apidechkul T. Comparison of quality of life and mental health among elderly people in rural and suburban areas, Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2011; 42(5): 1282.
- Kosulwit L. Mental health status, including depression and quality of life among members of an elderly club in suburban Bangkok. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012; 95(1): 92-101.
- Turner III DW. Qualitative interview design: A practical guide for novice investigators. The Qualitative Report. 2010; 15(3): 754.
- Hsieh FY, Bloch DA, Larsen MD. A simple method of sample size calculation for linear and logistic regression. Stat Med. 1998; 17(14): 1623-1634.
- Ministry of Public Health. Geriatric Medicine. 2019.
- Bhattacharjee S, Lee JK, Vadiei N, Patanwala AE, Malone DC, Knapp SM, et al. Extent and Factors Associated with Adherence to Antidepressant Treatment During Acute and Continuation Phase Depression Treatment Among Older Adults with Dementia and Major Depressive Disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020; 16: 1433.
- Chekani F, Holmes HM, Johnson ML, Chen H, Sherer JT, Aparasu RR. Use of Atypical Antipsychotics in Long-Term Care Residents with Parkinson’s Disease and Comorbid Depression. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2020; 12: 23.
- Wang J, Xiao LD, Li X. Health professionals’ perceptions of developing dementia services in primary care settings in China: a qualitative study. Aging Ment Health. 2019; 23(4): 447-454.
- Piyabhan P, Wetchateng T. Cognitive enhancement effects of Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi) on novel object recognition and VGLUT1 density in the prefrontal cortex, striatum, and hippocampus of sub-chronic phencyclidine rat model of schizophrenia. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013; 96(5): 625-632.
- Piyabhan P, Wetchateng T. Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi) Enhanced Cognitive Function and Prevented Cognitive Impairment by Increasing VGLUT2 Immunodensity in Prefrontal Cortex of Sub-Chronic Phencyclidine Rat Model of Schizophrenia. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015; 98: 7-15.
- Uabundit N, Wattanathorn J, Mucimapura S, Ingkaninan K. Cognitive enhancement and neuroprotective effects of Bacopa monnieri in Alzheimer's disease model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010; 127(1): 26-31.
- Saini N, Singh D, Sandhir R. Bacopa monnieri prevents colchicine-induced dementia by anti-inflammatory action. Metab Brain Dis. 2019; 34(2): 505-518.
- Saini N, Singh D, Sandhir R. Neuroprotective effects of Bacopa monnieri in experimental model of dementia. Neurochemical research. 2012; 37(9): 1928-1937.
- Deplanque D, Machuron F, Waucquier N, Jozefowicz E, Duhem S, Somers S, et al. Etifoxine impairs neither alertness nor cognitive functions of the elderly: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018; 28(8): 925-932.
- Poisbeau P, Gazzo G, Calvel L. Anxiolytics targeting GABAA receptors: Insights on etifoxine. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2018; 19(1): 36-45.
- Mattei C, Taly A, Soualah Z, Saulais O, Henrion D, Guérineau NC, et al. Involvement of the GABAA receptor α subunit in the mode of action of etifoxine. Pharmacol Res. 2019; 145: 104250.
- Poonsawang T, Kedthongma W, Phakdeekul W. Effectiveness of Practice Application for Postpartum Mothers. Test Eng Manag. 2020; 83: 16701-16704.
- Nueakhumung J, Phakdeekul W, Kedthongma W. Factor Effecting to Participation of Public Health Volunteers in Education Institution. Test Eng Manag. 2020; 83: 16230-16233.
- Van Patten R, Keller AV, Maye JE, Jeste DV, Depp C, Riek LD, et al. Home-based cognitively assistive robots: maximizing cognitive functioning and maintaining independence in older adults without dementia. Clin Interv Aging. 2020; 15: 1129.
- Batko-Szwaczka A, Wilczyński K, Hornik B, Janusz-Jenczeń M, Włodarczyk I, Wnuk B, et al. Predicting adverse outcomes in healthy aging community-dwelling early-old adults with the timed up and go test. Clin Interv Aging. 2020; 15: 1263.
- Chekani F, Holmes HM, Johnson ML, Chen H, Sherer JT, Aparasu RR. Use of Atypical Antipsychotics in Long-Term Care Residents with Parkinson’s Disease and Comorbid Depression. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2020; 12: 23.
Author Info
Wuttiphong Phakdeekul* and Warinmad KedthongmaReceived: 07-Jul-2021 Accepted: 21-Jul-2021 Published: 28-Jul-2021
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ARTICLE TOOLS
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Psychometric properties of the World Health Organization Quality of life instrument, short form: Validity in the Vietnamese healthcare context Trung Quang Vo*, Bao Tran Thuy Tran, Ngan Thuy Nguyen, Tram ThiHuyen Nguyen, Thuy Phan Chung Tran SRP. 2020; 11(1): 14-22 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- Deuterium Depleted Water as an Adjuvant in Treatment of Cancer Anton Syroeshkin, Olga Levitskaya, Elena Uspenskaya, Tatiana Pleteneva, Daria Romaykina, Daria Ermakova SRP. 2019; 10(1): 112-117 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.19
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Manilkara zapota (L.) Royen Fruit Peel: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review Karle Pravin P, Dhawale Shashikant C SRP. 2019; 10(1): 11-14 » doi: 0.5530/srp.2019.1.2
- Pharmacognostic and Phytopharmacological Overview on Bombax ceiba Pankaj Haribhau Chaudhary, Mukund Ganeshrao Tawar SRP. 2019; 10(1): 20-25 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.4
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- A Prospective Review on Phyto-Pharmacological Aspects of Andrographis paniculata Govindraj Akilandeswari, Arumugam Vijaya Anand, Palanisamy Sampathkumar, Puthamohan Vinayaga Moorthi, Basavaraju Preethi SRP. 2019; 10(1): 15-19 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3