Short Communication - (2022) Volume 13, Issue 10
Abstract
Fighting against the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus is one of the most critical challenges facing the global health system today. The possibility to identify the group of persons in the cohort of people under 50 years old, who are sensitive to the Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) disease by non-invasive methods, is a very perspective approach for estimating the epidemiological state of the human population. The study aimed to identify the features of people’s faces with COVID-19 that the most correlate with disease severity could serve as one of these approaches. For this aim, 525 photos of patients’ faces with different outcomes of COVID-19 disease were analyzed using the Dlib face recognition convolutional neural network pre-trained for face recognition. Face descriptor vectors were obtained using the convolutional neural network. Facial features were found that predict a person’s sensitivity to the SARS- CoV-2 virus (disease severity), and the contribution of each of the features to the risk of developing a severe form of COVID in a person was found. The accuracy of the binary classification of the individual severity of the COVID-19 course using the K-Nearest Neighbor’s (KNN) algorithm on the test dataset was accuracy-84%, Area under the Curve (AUC)-0.90.
Keywords
SARS-CoV-2 virus, COVID-19 disease, Face recognition
About the Study
The disease COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus, is one of the most pressing challenges of modern medicine (Hu B, et al., 2021). To date, the SARS-CoV-2 virus has infected about 160 million people and caused 3 million deaths (Worldometer, 2021). In most cases, the severe course of COVID-19 with a fatal outcome is observed in older people (Worldometer, 2021). In total, young and middle-aged people fall ill as a result of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the same percentage as the elderly (over 50 years old). Due to new mutations of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the COVID-19 disease affects an increasingly young age group with a more severe course of the disease (Thiagarajan K, 2021). Identifying the risk group among young and middle-aged people susceptible to COVID-19 is an important prerequisite for tackling the pandemic. Modern methods of analyzing photographs of a face in order to determine the phenotypic features of various diseases are increasingly used in the diagnosis of such diseases as cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and cancer (Kotanidis CP and Antoniades C, 2020; Ang L, et al., 2021; Liang B, et al., 2020).
Our study used randomly selected photographs of the faces of young, middle-aged, and older people (from 18 to 102 years old) of different sexes (264 women and 261 men) and different ethnic groups. 95% of the dataset was made up of photographs of faces of Caucasians who fell ill with COVID-19 with positive and negative outcomes. Among them were 261 with negative and 264 with positive anamneses taken from the Internet resources (Yee L, 2021; Wurzburger A, 2021). The obtained dataset contains 525 photos. All photographs of the patients’ faces were processed at the initial stage using the pre-trained convolutional neural network Dlib face recognition from the Deepface library to extract face descriptor vectors. Pre-trained neural network (modification of ResNet-34) has computed 128-dimensional face descriptor vectors. After converting patients’ faces to face descriptor vectors in MATLAB, using chi-square tests and the Maximum Relevance-Minimum Redundancy (MRMR) algorithm, six facial features 117, 100, 52, 92, 24, and 67 were selected that were most correlated with the outcome COVID-19 disease. After interpreting these features, it was found that the values of 24 and 67 features are most correlated with the age and sex of the patient, respectively. For 52 and 92 features, the PCA method yielded a single generalized feature, the value of which most correlated with the patient’s ethnicity and disease outcome (the highest values of this feature were in black and asians). Using the six obtained features, the K-Nearest Neighbor’s (KNN) algorithm was trained for the binary classification problem. The classification accuracy on the test dataset was 84%, AUC-0.90. These values characterize the good performance of this classifier in Figure 1.
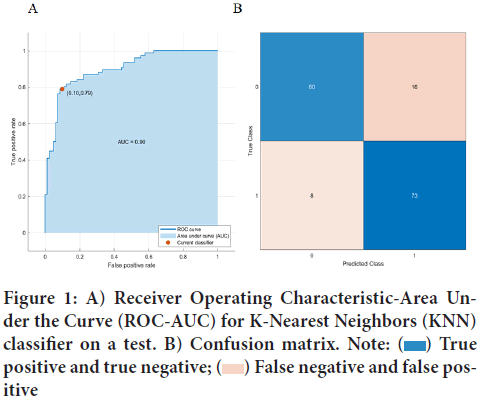
Figure 1: Receiver Operating Characteristic-Area Under the Curve (ROC-AUC) for K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
classifier on a test. B) Confusion matrix. Note:  True
positive and true negative;
True
positive and true negative;  False negative and false positive
False negative and false positive
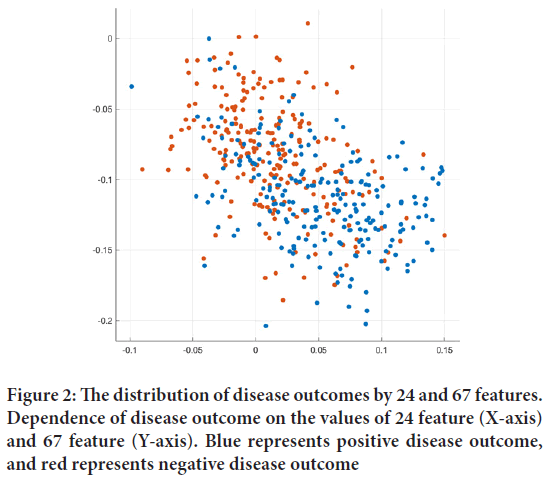
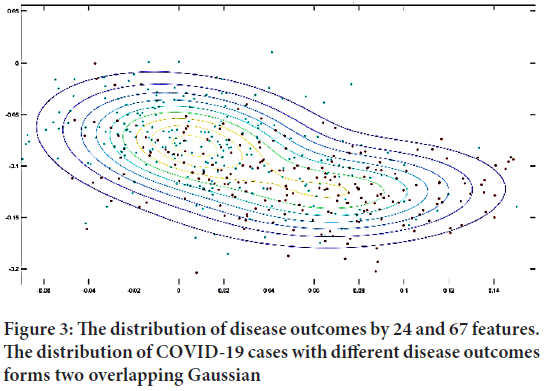
Determination of phenotypic features associated with the anatomical features of the face and the search for their correlations with susceptibility (severity of the course of the disease) to the SARS-CoV-2 virus is an essential task for modern data analysis. The use of methods for analyzing biomedical data (in particular, facial images) makes it possible to find phenotypic features that are reliably associated with the individual severity of the course of the COVID-19 disease. As a result of the analysis of photographs of the faces of people with COVID-19, three features were found, listed in the order of their influence on the risk of negative disease outcome: Age, ethnicity, and sex of the patient. The dependence of disease outcome on age (24 features) and sex (67 features) is shown in Figures 2 and 3. This shows that the distribution of COVID-19 cases with different disease outcomes forms two overlapping Gaussian. If they take photographs of the face of the same patient at different ages, then the position of the point is shifted along the isolines in the space of these two features. Epidemiological data support our results that the severity of COVID significantly depends on the patient’s age, sex, and ethnicity. The risk of negative disease outcome strongly correlates with Asian ethnicity has been the research subject since the beginning of 2020. In particular, the level of ACE2 expression in the lung tissues of Asians (Zhao Y, et al., 2020) and the found genetic predisposition to coronaviruses in Asians (Souilmi Y, et al., 2021) are mentioned.
Figure 2: The distribution of disease outcomes by 24 and 67 features. Dependence of disease outcome on the values of 24 feature (X-axis) and 67 feature (Y-axis). Blue represents positive disease outcome, and red represents negative disease outcome
Figure 3: The distribution of disease outcomes by 24 and 67 features. The distribution of COVID-19 cases with different disease outcomes forms two overlapping Gaussian
Conclusion
A method was developed for assessing the individual sensitivity of patients of different ages, sex, and ethnicity to the disease COVID-19. A classifier with a high predictive accuracy of disease outcome was built using the patient’s facial features. Facial features were found that predict a person’s sensitivity to the SARS-CoV-2 virus (disease severity), and the contribution of each of the features to the risk of developing a severe form of COVID in a person was found.
References
- Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021; 19(3): 141-154.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Worldometer. Coronavirus cases. Worldometer. 2021.
- Worldometer. Age, sex, existing conditions of COVID-19 cases and deaths. Worldometer. 2021.
- Thiagarajan K. Why is India having a COVID-19 surge?. BMJ. 2021; 373: 1124.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Kotanidis CP, Antoniades C. Selfies in cardiovascular medicine: Welcome to a new era of medical diagnostics. Eur Heart J. 2020; 41(46): 4412-4414.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Ang L, Yim MH, Do JH, Lee S. A novel method in predicting hypertension using facial images. Appl Sci. 2021; 11(5): 2414.
- Liang B, Yang N, He G, Huang P, Yang Y. Identification of the facial features of patients with cancer: A deep learning-based pilot study. J Med Internet Res. 2020; 22(4): 17234.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Yee L. Stars who have tested positive for Coronavirus (Photos). The Wrap. 2021.
- Wurzburger A. Celebrities we lost to COVID-19. People. 2021.
- Zhao Y, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Ma Y, Zuo W. Single-cell RNA expression profiling of ACE2, the putative receptor of Wuhan 2019-nCov. BioRxiv. 2020.
- Souilmi Y, Lauterbur ME, Tobler R, Huber CD, Johar AS, Moradi SV, et al. An ancient viral epidemic involving host coronavirus interacting genes more than 20,000 years ago in East Asia. Curr Biol. 2021; 31(16): 3504-3514.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
Author Info
Oleg Kit*Citation: Kit O: Face Biometrics as a Potential Predictor for COVID-19 Susceptibility
Received: 15-Sep-2022 Accepted: 10-Oct-2022 Published: 17-Oct-2022, DOI: 10.31858/0975-8453.13.10.656-657
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ARTICLE TOOLS
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Psychometric properties of the World Health Organization Quality of life instrument, short form: Validity in the Vietnamese healthcare context Trung Quang Vo*, Bao Tran Thuy Tran, Ngan Thuy Nguyen, Tram ThiHuyen Nguyen, Thuy Phan Chung Tran SRP. 2020; 11(1): 14-22 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- Deuterium Depleted Water as an Adjuvant in Treatment of Cancer Anton Syroeshkin, Olga Levitskaya, Elena Uspenskaya, Tatiana Pleteneva, Daria Romaykina, Daria Ermakova SRP. 2019; 10(1): 112-117 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.19
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Manilkara zapota (L.) Royen Fruit Peel: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review Karle Pravin P, Dhawale Shashikant C SRP. 2019; 10(1): 11-14 » doi: 0.5530/srp.2019.1.2
- Pharmacognostic and Phytopharmacological Overview on Bombax ceiba Pankaj Haribhau Chaudhary, Mukund Ganeshrao Tawar SRP. 2019; 10(1): 20-25 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.4
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- A Prospective Review on Phyto-Pharmacological Aspects of Andrographis paniculata Govindraj Akilandeswari, Arumugam Vijaya Anand, Palanisamy Sampathkumar, Puthamohan Vinayaga Moorthi, Basavaraju Preethi SRP. 2019; 10(1): 15-19 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3