Research Article - (2021) Volume 12, Issue 11
Optimum Composition of Developed Additive Based Insect Repellent Paint
Zeeshan Ahmada1*, Faiza Hassanb2, Sana Noorc3, Munir Ahmadd4 and Khalid Rashide5Abstract
Active compounds of Cymbopogon winterianius, Cymbopogoncitratus, Rosmarinus officinalis, Cedrus, and Eugenol, have been reported to have different insect repellant compounds. Control and development of natural insect repellent additive based decorative coating has driven this work to incorporate the essential oils with long chain fatty acids in water-based lab developed conventional paint. In this work, the Additive based Paint was formulated and its ability to repel different insects was determined. The optimum composition of developed additive-based paint was determined by three standard paint analyses which were adhesion, elasticity and insect repellency. As per challenge of Pigment powder and Polymer use for such paint is achieved by testing on Latest instruments. The best composition of additive in paint was found to be 15%. Where it able to repel Pavement Ants, non-biting Flies, Mosquitoes and Black field ant with 80% efficiency. It is envisioned that the formulated paint is effectively function as insect repellent thus as an alternative way to reduce the insect-borne diseases.
Keywords
Insect repellent, Additives, Optimum composition, Insect-borne diseases
Introduction
Arthropod bites remain a major cause of patient morbidity. These bites can cause local or systemic effects that may be infectious or inflammatory in nature. Arthropods, notably insects and arachnids, are vectors of potentially serious ailments including malaria, West Nile virus, dengue, and Lyme disease (Rajagopalan R, 1989). Synthetic organic insecticides used to control insects have produced a feedback of environmental ill effect, non-targets organisms being affected and most mosquito species have becoming physiologically resistant to synthetic insecticides (Katz TM, et al., 2008). The application of synthetic repellents may cause allergic to some of people. Higher concentration or frequent application of N, N-Diethyl-3-Methylbenzamide (DEET) exposure causes insomnia, mood disturbances and impaired cognitive function (Lietman PS, et al., 1980). While, Plant essential oils have many useful applications beyond those in the fragrance and flavoring industries, among which are their uses as pesticides and insect repellents. An emerging body of scientific literature reports the efficacy of various essential oils for use against pests of public health, stored product pests, and agricultural pests (Pavela R and Benelli G, 2016). Generally, EOs cause neurotoxic effects in insects (Morgans WM, 1990). The current study reports the composition and insect repellent activity of a latex coating made by using essential oils from Citronella (winterianius), Cymbopogon citratus, Rosmarinus officinalis, Lemongrass, Cedrusand Eugenol against several reported insects (Figure 1). Paint is a liquid which spreads over a substrate in the form of thin layer and it is transformed into a solid adherent film (Brock T, et al., 2000). There are two major functions of paint. One protection and other is decoration. The earliest known use of paints dates back more than 30,000 years to cave paintings in Spain (Goldschmidt A and Streitberger HJ, 2007).
Figure 1: Chemical structures of essential oil
Differences in the composition of the various coatings systems are presented in Table 1. Common to all three coating systems are the resin and additive (Lambourne R and Strivens TA, 1999).
| Material Cat- egory | Coating Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pigmented paint | Powder coating | Clear coat | |
| Resin | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Additive | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Solvent | Yes | No | Yes |
| Pigment and extender | Yes | Yes | No |
Table 1: Typical composition of various coating systems
Materials and Methods
Distilled water and all other Paint related chemicals were purchased by Sheikh Traders Lahore, Rutile grade titanium dioxide pigment manufactured by the chloride process for both interior and exterior coatings applications prepared by Ti-Pure is used. Fine powdered CaCO3 and Talcum was provided by Shaheen Grinding Mills. Other chemicals are as, Thickener from Ashland Chemical Company America, Ammonia solution of Petrokemija from Croatia.
Dispersing agent of BASF chemical company is used. two Biocides one for in can preservation named Parmetol DF-35 by Schulke and other one for dry film preservation named Preventol A-14D by LANXESS. Anti-foam for water-based coating developed by Blackburn Chemicals is used Monoethylene Glycol (MEG) and UCAR Filmer IBT by DOW Chemicals is used. Acrylic Binder of Code 1229 from Power Chemical Industries is used. Essential Oils were obtained through Attar Oils made by USA. Soya oil is used as long chain fatty acid along with KOH.
KOH salt of long chain fatty acids
At first step take water in Glass beaker and add KOH under proper stirring to make a lye solution. Took Long Chain Fatty Acid in a Glass Beaker and pour Lye solution in it with continuous stirring. Now place the beaker on hot plat to let it boil gently, Keep stirring to avoid spattering of potassium hydroxide solution while using a gentle heat and keep constant stirring. Continue boiling until water evaporates and it starts harden. After 30 minutes at 60°C-70°C it become jell type structure then place it at room temperature to cool with constant stirring. After proper mixing cool it and pack it in air tight jar (Table 2).
| Chemicals | Dosage |
|---|---|
| KOH | 38% |
| Long Chain Fatty Acid | 30% |
| Water | 32% |
Table 2: Composition for Potassium salt of long chain fatty acids
Additive preparation
Citronella oil is one of the most widely used natural insect repellents. So, pre mixture of others Essential oils in Citronella Oil is made up using percentages mentioned in Table 3.
| Chemicals | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Citronella Oil | 82.35 |
| Cedar Oil | 5.88 |
| Rosemary Oil | 5.88 |
| Eugenol Oil | 3.52 |
| Lemongrass Oil | 2.35 |
| Total | 100 |
Table 3: Pre mix of essential oils
Then 30% Potassium Hydroxide salt of long chain fatty acids is mixed with 70% of Essential oils premix for finalizing insect Repellent Additive.
Insect repellent emulsion
Conventional Water based latex emulsion was prepared up as per previously reported method. Six different samples were made with different percentages of added additive, and marked as bellow (Table 4).
| Sample | Code Name |
|---|---|
| 5% Additive | A-1 |
| 4% Additive | B-3 |
| 3% Additive | C-2 |
| 2% Additive | D-4 |
| 5% Potassium Soap Of long chain Fatty Acids | E-5 |
| No Additive | F-6 |
Table 4: Sample coding
Results and Discussion
Field test for ants
Ants leave pheromones after them and it helps them find their way back to the nest. Calcium carbonate interferes with the navigational system of ant and prevents them from following pheromone trail left behind earlier. The necessary oils get absorbed by smell receptors.
These receptors are located in the ant’s nose and smells head towards brain’s limbic system. It is this part of the ant’s body that controls all the movements of the ant through mood, memory, emotions etc. Thus, the oils used keep the ants away from the coatings (Figure 2).
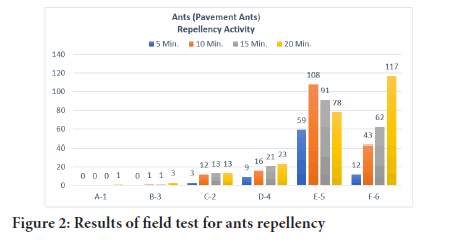
Figure 2: Results of field test for ants repellency
Figure 2 describes the results of ant’s repellency test as sample A1 with 20% Additive shows the best results at which only one ant appears in 20 minutes. B3 shows good resistance better than C2 but less effective than A1 as there were 3 ants in starting after 5 minutes at C2 while there was not a single ant at B3. After 20 minutes only 3 ants come at B3 and counting at C2 was 13. Gradually D4 is better than F6 and E5 as contain only 2% additive. At E5 initially observed more ants than F6 but with passing time ants preferred to move from that coating, in case of F6 inverse case of E5 is observed (Figure 3).

Figure 3: Ants repellency
Cage test for flies
The Eugenoloil, used, has natural Permethrin, proving best as flies repellant. Figure 4 describes the results of non-biting flies test performed in a glass Squair and note the landing flies on coated surface after different time intervals, we found that there was only 1 fly land on A1 formula coated surface in 10 minutes and only 2 flies in 20 minutes. All others formulas results are comparable as in initial five minutes there was 1 fly landed on B3, 2 flies on C2, 2 flies on D4, 4 flies on E5 and 3 flies on F6. After 10 minutes the counting was 3,3,4 and 4 flies simultaneously. Sample A1 resist better than all other samples due to presence of higher concentration of Eugenol (Figures 4 and 5).
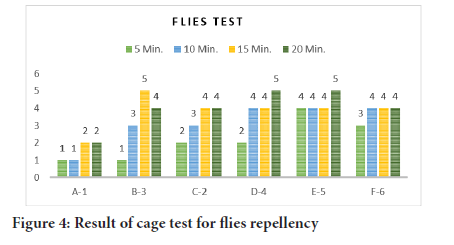
Figure 4: Result of cage test for flies repellency

Figure 5: House hold flies test
Cage test for mosquitoes
Mosquitoes have acute receptors on their antennae, head etc. These receptors can direct the mosquitoes from one hundred feet distance. Scents are mainly responsible and helpful source for mosquitoes tempting them to prey. Citronella masks these scents which cause attraction for mosquitoes towards lactic acid, saccharides, carbon dioxide, blood etc. Higher concentration proves great repellence of mosquitoes as is shown in Figure 6 only one Mosquito was landed after 20 minutes on A1. B3 and C2 resist against mosquitoes better than E5 and F6 (Figures 6 and 7).
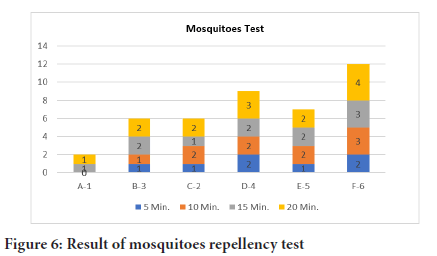
Figure 6: Result of mosquitoes repellency test
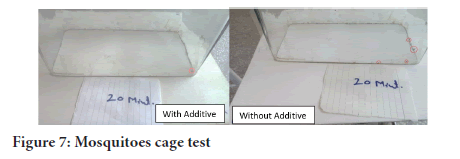
Figure 7: Mosquitoes cage test
Black field ants
Black field ants (Carpenter ants) are also tested on coated plates and found only 1 Black field ant at start but it also leaves the surface in 15 minutes and did not come back even after 20 minutes, while B3, C2 and D4 also resist better one reason is of such good results is also that all these coated plates are tested with comparison of F6 (Blank) so Black field ant prefer to be at F6 than any other because all other have some amount of repellent additive (Figure 8).
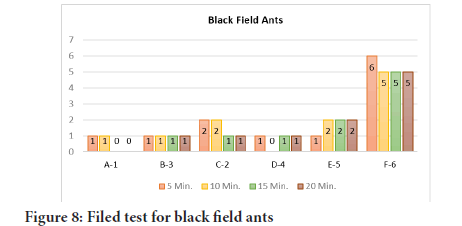
Figure 8: Filed test for black field ants
Scrub resistance
Figure shows the application of manufactured paint at standard black scrub sheet with 200 μm Film applicator as per Standard ASTM D4213 and 2486.The concentrated paints with VOC may cause loss of scrub resistance. There are different scrub tests for varying paint products identified to be conventional interior paints. The convention interior paints can manage to resist upto 16 scrubs and the exterior paint can go good against upto 4000 scrubs with only a little loss of gloss.
The concentrated paints with VOC may cause loss of scrub resistance. There are different scrub tests for varying paint products identified to be conventional interior paints. The convention interior paints can manage to resist upto 16 scrubs and the exterior paint can go good against upto 4000 scrubs with only a little loss of gloss. The concentrated paints with VOC may cause loss of scrub resistance. There are different scrub tests for varying paint products identified to be conventional interior paints. The convention interior paints can manage to resist upto 16 scrubs and the exterior paint can go good against upto 4000 scrubs with only a little loss of gloss (Table 5).
| S. No | Paint | Manufactured on | 200 µm film applied on Black Sheets | Scrubs Checked on Scrub Tester Machine | Weight of Sheet Before Scrubs (g) | Weight of Sheet After Scrubs (g) | Difference in Weight (g) | Scrubs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A-1 | 23/3/2018 | 27/4/2018 | 29/4/2018 | 30.002 | 28.637 | 1.365 | 18-24 |
| 2 | B-3 | 23/3/2018 | 27/4/2018 | 29/4/2018 | 30.008 | 28.712 | 1.296 | 17-24 |
| 3 | C-2 | 23/3/2018 | 27/4/2018 | 29/4/2018 | 30.006 | 28.740 | 1.266 | 18-24 |
| 4 | D-4 | 23/3/2018 | 27/4/2018 | 29/4/2018 | 30.001 | 28.734 | 1.267 | 17-24 |
| 5 | E-5 | 23/3/2018 | 27/4/2018 | 29/4/2018 | 30.003 | 28.742 | 1.261 | 15-24 |
| 6 | F-6 | 23/3/2018 | 27/4/2018 | 29/4/2018 | 30.002 | 28.745 | 1.257 | 19-24 |
Table 5: Results of washability of paint samples
Result of these scrubs sheets are above in table; it is observed that even with 5% Additive its Scrubs are in limits as film starts rupturing at 18th scrub and completely tor at 24th scrubs. So, all other sheets are checked for 24 scrubs. The difference in weight loss is comparable (Figure 9).

Figure 9: Sheets after scrub testing
MFFT of binder
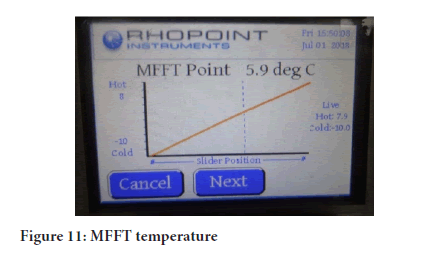
Higher MFFT causes hardness of the polymer and there will be less of thermoplastic polymer. Thus, there is least chance for the dust particles to land, adhere and stay on the paint film. Increased amount of dust accumulation causes attraction for the insects onto the paint film and vice versa meaning less accumulation of dirt saves paint surface from insects. Binder was tested on Rohpoint Minimum Film Forming Temperature machine and found the 5.9ºC (Figures 10 and 11).

Figure 10: Film formation
Figure 11: MFFT temperature
Conclusion
By all experimental study, found that the paint having additive based on potassium salt of long chain fatty acid and blend of citronella oil along with four other abovementioned oils has successfully worked as repellent of pavement ants, non-biting Flies, mosquitoes and black field ant with 80% efficiency. It is envisioned that the formulated paint is effectively function as insect repellent thus as an alternative way to reduce the insect-borne diseases. The 15% additive containing paint formulation has the best condition by giving good adhesion and 80% effective insect repelling time.
Author’s Contributions
Zeeshan Ahmad: Formulation of Additive & Emulsion Paint has been developed by Zeeshan Ahmad.
Faiza Hassan: Supervise the research and all related materials are arranged by Faiza Hassan.
Sana Noor: Optimization of additive dosage in paint has been done by Sana Noor.
Munir Ahmad: All Testing’s are suggested and designed.
Khalid Rashid: Testing’s are conducted and results are noted by Khalid Rashid.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank and sincerely acknowledge the help of supervisor Dr. Faiza Hassan, Coordinator Department of Chemistry, University of Lahore, her continuous and consistent guidance, support and encouragement gave us a real motivation in doing this project.
References
- Rajagopalan R. Vector control research centre. Misc Publ. 1989.
- Katz TM, Miller JH, Hebert AA. Insect repellents: historical perspectives and new developments. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 58(5): 865-871.
- Lietman PS, Heick HM, Shipman RT, Norman MG, James W. Reye-like syndrome associated with use of insect repellent in a presumed heterozygote for ornithine carbamoyl transferase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1980; 97(3): 471-473.
- Pavela R, Benelli G. Essential oils as ecofriendly biopesticides? Challenges and constraints. Trends Plant Sci. 2016; 21(12): 1000-1007.
- Morgans WM. Outlines of paint technology. Griffin. 1990.
- Brock T, Groteklaes M, Mischke P. European coatings handbook. Vincentz Network. 2000.
- Goldschmidt A, Streitberger HJ. BASF Handbook on Basics of Coating Technology. Vincentz Network. 2007; 345-401.
- Lambourne R, Strivens TA. Paint and surface coatings: Theory and practice. Elsevier. 1999.
Author Info
Zeeshan Ahmada1*, Faiza Hassanb2, Sana Noorc3, Munir Ahmadd4 and Khalid Rashide52Department of Chemistry, University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
3Department of Chemistry, University of Central Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
4Department of Medical Physics, INMOL Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
5Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, PCSIR Labs complex, Lahore, Pakistan
Received: 26-May-2021 Accepted: 09-Jun-2021 Published: 16-Jun-2021
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ARTICLE TOOLS
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Psychometric properties of the World Health Organization Quality of life instrument, short form: Validity in the Vietnamese healthcare context Trung Quang Vo*, Bao Tran Thuy Tran, Ngan Thuy Nguyen, Tram ThiHuyen Nguyen, Thuy Phan Chung Tran SRP. 2020; 11(1): 14-22 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- Deuterium Depleted Water as an Adjuvant in Treatment of Cancer Anton Syroeshkin, Olga Levitskaya, Elena Uspenskaya, Tatiana Pleteneva, Daria Romaykina, Daria Ermakova SRP. 2019; 10(1): 112-117 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.19
- Dental Development between Assisted Reproductive Therapy (Art) and Natural Conceived Children: A Comparative Pilot Study Norzaiti Mohd Kenali, Naimah Hasanah Mohd Fathil, Norbasyirah Bohari, Ahmad Faisal Ismail, Roszaman Ramli SRP. 2020; 11(1): 01-06 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2020.1.01
- Manilkara zapota (L.) Royen Fruit Peel: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review Karle Pravin P, Dhawale Shashikant C SRP. 2019; 10(1): 11-14 » doi: 0.5530/srp.2019.1.2
- Pharmacognostic and Phytopharmacological Overview on Bombax ceiba Pankaj Haribhau Chaudhary, Mukund Ganeshrao Tawar SRP. 2019; 10(1): 20-25 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.4
- A Review of Pharmacoeconomics: the key to “Healthcare for All” Hasamnis AA, Patil SS, Shaik Imam, Narendiran K SRP. 2019; 10(1): s40-s42 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1s.21
- A Prospective Review on Phyto-Pharmacological Aspects of Andrographis paniculata Govindraj Akilandeswari, Arumugam Vijaya Anand, Palanisamy Sampathkumar, Puthamohan Vinayaga Moorthi, Basavaraju Preethi SRP. 2019; 10(1): 15-19 » doi: 10.5530/srp.2019.1.3